Advanced Typescript - 타입스크립트 좀더 깊게 알아보기
Intersection Type (교차 타입)
type Admin = {
name: string;
privileges: string[];
};
type Employee = {
name: string;
startDate: Date;
};
type ElevatedEmployee = Admin & Employee;
const e1: ElevatedEmployee = {
name: 'Max',
privileges: ['create-server'],
startDate: new Date()
};
type Combinable = string | number;
type Numeric = number | boolean;
type Universal = Combinable & Numeric;
const u: Universal = 10;
const u2: Universal = false; // Error
const u3: Unviersal = '10'; // Error
custom type을 선언하여 & 연산자를 사용하여 새로운 type을 만들 때는 합집합이 됩니다.
하지만 union type 을 사용하여 string | number와 number | boolean의 타입을 & 연산자로
하나의 타입으로 만들 때는 교집합으로 이루어 집니다.
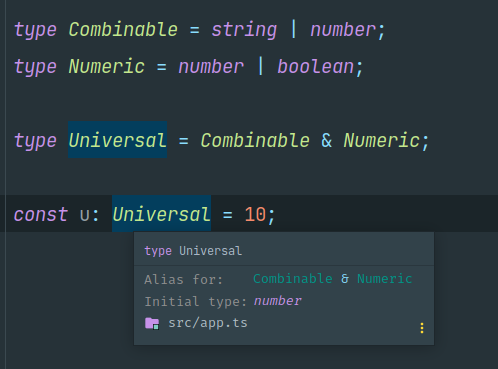
Initial type 이 number 인 것을 확인할 수 있습니다.
TypeGuard - 런타임에서 조금 더 안전하게 타입 사용하기
type Admin = {
name: string;
privileges: string[];
};
type Employee = {
name: string;
startDate: Date;
};
type ElevatedEmployee = Admin & Employee;
const e1: ElevatedEmployee = {
name: 'Max',
privileges: ['create-server'],
startDate: new Date()
};
type UnknownEmployee = Employee | Admin;
function printEmployeeInformation(emp: UnknownEmployee) {
console.log('Name: ' + emp.name);
// 사용자 정의 유형은 Typescript 에만 존재함으로 이렇게 비교할 수 없음
// if (typeof emp === 'Employee')
// privileges 가 emp 의 property 인지 확인한다.
if ('privileges' in emp) {
console.log('Privileges: ' + emp.privileges);
}
if ('startDate' in emp) {
console.log('Start Date: ' + emp.startDate);
}
}
printEmployeeInformation(e1);
관리자 타입과 일반 직원 타입 둘 다 가질 수 있는 UnknownEmployee 타입이 있습니다.
type의 속성들을 출력하는 함수를 만들었는데 관리자 타입인지 직원 타입인지 를 컴파일에서 알 수 없기 때문에
컴파일이 되어도 런타임에서 에러가 발생할 수 있습니다.
이를 사전에 방지하고자 type guard를 사용해 좀 더 안전하게 코딩을 하려고 합니다.
if (typeof emp === 'Employee') // X
if (typeof emp === 'object') // O이렇게 파라미터 값을 직접 typeof로 비교하면 되지 않을까 싶지만 커스텀 타입은 javascript 에는 존재하기 않기 때문에 비교할 수 없습니다.
그렇다면 어떻게 비교해야 할까?
// privileges 가 emp 의 property 인지 확인한다.
if ('privileges' in emp) {
console.log('Privileges: ' + emp.privileges);
}
in 연산자를 사용하여 privileges라는 key 가 emp 안에 존재하는지 여부를 체크합니다.
하지만 string으로 검사를 하다 보면 사람이 실수를 할 수 도 있고 2% 부족한 감이 없지 않아 있습니다.
명시적으로 type 검사하기
class Car {
drive() {
console.log('Driving...');
}
}
class Truck {
drive() {
console.log('Driving a truck...');
}
loadCargo(amount: number) {
console.log('Loading cargo... ' + amount);
}
}
type Vehicle = Car | Truck;
const v1 = new Car();
const v2 = new Truck();
function useVehicle(vehicle: Vehicle) {
vehicle.drive();
if (vehicle instanceof Truck) {
vehicle.loadCargo(1000);
}
}
useVehicle(v1);
useVehicle(v2);
instanceof라는 keyword를 사용하여 런타임 환경에서 v1이라는 인스턴스가 어떤 클래스로 만들어졌는지를 검사합니다.
javascript 에도 존재하기 때문에 이것이 가능합니다.
Union Type 식별하기
interface Bird {
type: "bird";
flyingSpeed: number;
}
interface Horse {
type: "horse";
runningSpeed: number;
}
type Animal = Bird | Horse;
function moveAnimal(animal: Animal) {
let speed;
switch (animal.type) {
case "bird":
speed = animal.flyingSpeed;
break;
case "horse":
speed = animal.runningSpeed;
break;
default:
break;
}
console.log("Moving at speed: " + speed);
}
interface로 구현된 타입들의 Union Type 은 Class처럼 javascript 에는 존재하지 않는 타입의 형태 이기 때문에
if (animal instanceof Bird) {}와 같이 인스턴스로 구분할 수가 없다.
그렇다고 string으로 구분을 하자니 이건 우리가 지양하는 타입이니 좀 더 좋은 방법이 없을까?
위에서 보다시피 type이라는 key에 리터럴 한 값을 집어넣었다. 이건 tyepscript에서 말하는 type 은 아니지만 런타임 환경에서도 if문 또는 switch 문에서 사용할 수 있는 type 은 확실하다.
typescript의 타입 추론 덕분에
case 'bird':
// animal.runningSpeed 가 오면 불만을 표출한다.
case 'bird'라는 스코프 안에서는 animal의 type 이 Bird라는 것을 추론하여 Horse의 property 가 오면 에러를 발생시킨다.
이것이 typescript의 장점인 것 같다.
Type casting
typescript로 개발을 하다 보면 우린 분명 이 것에 대한 type을 알고 있는데 type 추론은 이것을 알지 못할 때가 있다.
const inputTag = document.getElementById("user-input")!;
inputTag.value = "user1"; // Error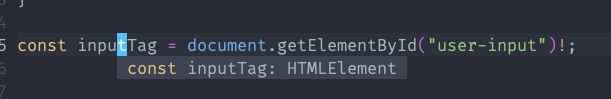
type 추론은 이것을 HTMLElement로 생각한다. 개발자들의 의도는 이것은 분명 input tag를 의도하고 쓴 거 겠지만 아쉽게도 추론에 실패했다.
이렇게 된 경우 타입 캐스팅으로 타입을 명시적으로 변환해야 한다.
타입 캐스팅엔 두 가지 방법이 있다.
const inputTag = <HTMLInputElement>document.getElementById("user-input")!;
const inputTag2 = document.getElementById("user-input")! as HTMLInputElement;
inputTag.value = "user1";
inputTag2.value = "user2";꺽쇠를 사용해 타입 캐스팅하는 방법과 as를 사용해 타입 캐스팅을 하는 방법이다.
요기서! 느낌표의 역할이 뭐냐고 물어보시는 분들이 있을 수도 있다.
user-input의 id를 가진 element를 가져올 때 이것은 null 일 수도 있고 inputelement 일수도 있다.
그래서 우리는! 를 달아 줌으로써 컴파일러에게 이건 null 이 아니라고 말해 주는 것이다.
if 문 사이에 넣는 것과 동일 한 효과다.
'TypeScript' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Typescript Generic programing (0) | 2021.11.29 |
|---|---|
| Advanced Typescript 2 (0) | 2021.11.29 |
| Typescript Interface (0) | 2021.11.28 |
| Typescript Class (0) | 2021.11.27 |
| typeorm database migration (0) | 2021.06.24 |
댓글
이 글 공유하기
다른 글
-
Typescript Generic programing
Typescript Generic programing
2021.11.29 -
Advanced Typescript 2
Advanced Typescript 2
2021.11.29 -
Typescript Interface
Typescript Interface
2021.11.28 -
Typescript Class
Typescript Class
2021.11.27